DNS Conditional forwarders
DNS conditional forwarders allow organizations to configure specific DNS servers to forward queries for specific domain names to designated forwarder servers. Unlike traditional forwarders that forward all DNS queries, conditional forwarders provide more control and granularity in directing DNS traffic.
The following blog post applies specifically to Microsoft DNS.
Export DNS conditional forwarders
The DNS PowerShell module does not include the Get-DnsServerConditionalForwarderZone (why, Microsoft, why?). Therefore, we need to use an alternative method.
To export your current DNS conditional forwarders to a CSV file, you can use the following command:
Get-DnsServerZone | Where-Object {$_.ZoneType -eq 'Forwarder'} | Export-Csv -NoTypeInformation DNSConditionalForwarders.csvIf you want to export conditional forwarders from another DNS server, use Get-DNSServerZone -ComputerName otherDNSName.
Import DNS conditional forwarders
To import the DNS conditional forwarders to your new DNS server , use the following code:
$csv = Import-Csv DNSConditionalForwarders.csv
foreach($zone in $csv){
try{
Add-DnsServerConditionalForwarderZone -Name $zone.ZoneName -MasterServers $zone.MasterServers -UseRecursion:([boolean]$zone.UseRecursion) -ForwarderTimeout $zone.ForwarderTimeout -ErrorAction stop
}
catch {
Write-Warning $($_.Exception.Message)
}
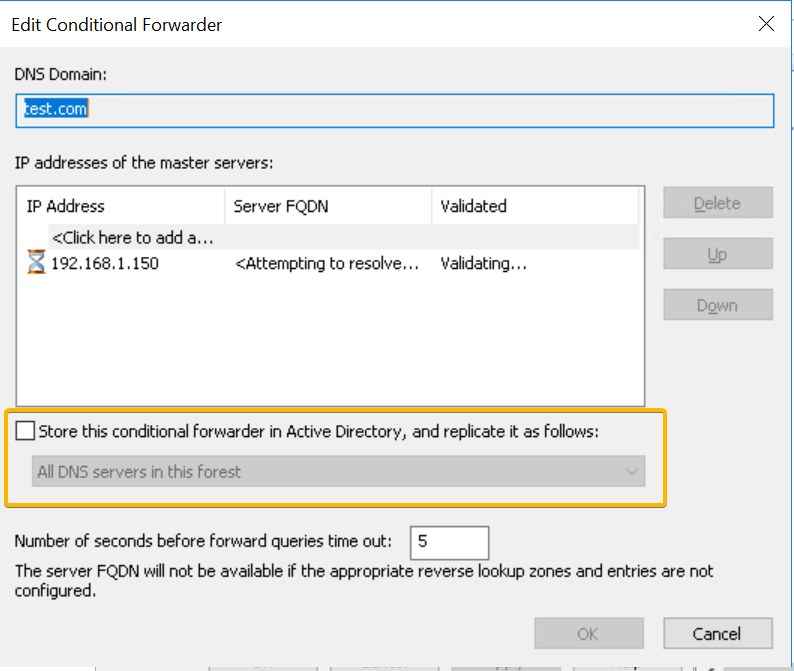
}Note: To prevent any issues, the script does not automatically set the IsDsIntegrated value for conditional forwarders. If you want to integrate the conditional forwarders into Active Directory, you need to set it manually. Follow these steps:
- Right-click on the conditional forwarders in the DNS management console.
- Select
Propertiesfrom the context menu. - In the Properties window, click on the
Editbutton. - Check the
Store this conditional forwarder in Active Directoryoption. - Choose the appropriate option based on your needs.
- Click
OKto save the changes.



Comments